What is neuropathy?
The word neuropathy is derived from two parts: “neuro” referring to the nerve and “pathy” indicating disorder.
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that occurs when injury or disease damages your peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nerves are the nerves that originate from your brain and spinal cord, and extend to your skin, muscles and tissues.
The peripheral nervous system relays information between your body and the brain in the form of electrical impulses. Each nerve is made up of many connected cells called neurons that transmit these impulses.
Nerves are the communication lines of the body. Electrical signals from the brain travel through the nerves and give instructions to the various body parts. The body receives information from the environment through the senses and sends this information to the brain via the nerves.
However, damage to the nerves disrupts this which results in the condition called peripheral neuropathy and its various symptoms.
The types of nerves
There are three types of peripheral nerves; the first is motor nerves which regulate the movements of your body’s muscles, the second is sensory nerves which transmit sensations such as heat, vibration, touch and pain to the brain. The third is the autonomic nerves which regulate the activities of the internal organs and glands.
The majority of the peripheral nerves are responsible for sensations you feel such as touch, pain and temperature. There are literally millions of these nerve endings in your fingers, hands, toes and feet which are designed to keep you out of danger and away from the things that are hot, cold, sharp, etc.
These nerves to the muscles of the hands and feet, legs and arms (called motor nerves) help to control the numerous muscles and movements in these regions of the body. It would also be difficult to walk without knowing what your feet are standing on or to pick things up if you had no idea how hard you were gripping something. It would be difficult to move if the impulses weren’t transmitted to the muscles.
The nerves to the autonomic system are not under conscious control but respond to the environment so the body can function optimally. It controls such tasks as controlling the bladder, slowing down or speeding up the heart rate, constricting or dilating the pupils of the eye. It regulates blood pressure, sexual response and many other responses.
Peripheral nerve cells have three main parts: cell body, axons, and dendrites (or terminal). (See diagram below)
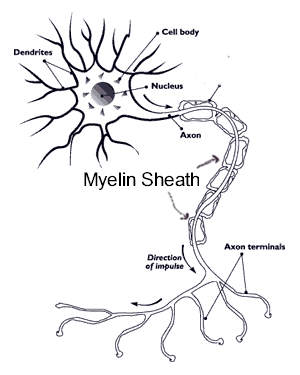
Damage to the nerves
Nerve damage or neuropathy normally occurs when the outer sheathing or the myelin (protective covering) of nerve cells degenerate. Without this protection the electrical signals are not transferred properly just like if you stripped the covering off of the electrical wires in your house.
As the nerve damage gets worse, the nerves either lose their ability to transmit information (numbness), or they start sending false signals (pain and tingling).
When the insulation begins to crumble, the unprotected “wire” will start short-circuiting.
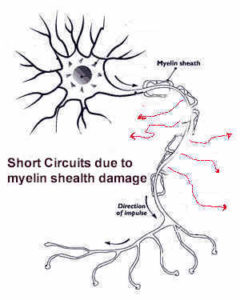
When the signal cannot be sent through the nerve, the area not receiving the messages will result in numbness.
Neuropathy is the condition where the nerves have sustained enough damage that there is noticeable numbness, pain or tingling.
How can you tell its neuropathy and not muscle or joint pain?
Difference between nerve pain and muscle pain:
- Muscle pain is preceded by trauma or injury, while nerve pain doesn’t (It can come from known trauma but not always).
- Muscle pain is an ache or pain in the muscle or joint, it feels achy and there can be stiffness, nerve pain or burning, stabbing and tingling.
- Muscle pain stops after healing of the injury takes place, nerve pain continues.
- Muscle and joint pain can be relieved with aspirin or other pain killers, the same medication does not help nerve pain.
Types of Nerves that can be Damaged
- Cranial: Nerves go from your brain to your eyes, mouth, ears and other parts of your head.
- Peripheral: Nerves go from your spinal cord to your arms, hands, legs and feet. This is the most common form of damage.
- Central: Nerves are in your brain and spinal cord.
- Autonomic: Nerves go from your spinal cord to your lungs, heart, stomach, intestines, bladder and sex organs. Damage to these nerves can create improper functioning of these organs.
Types of Neuropathy
There are three types: Mono Neuropathy, Poly Neuropathy and Autonomic Neuropathy or nerve damage.
Damage to a single nerve is called mononeuropathy. This usually results from injury or repeated stress. An example is carpal tunnel syndrome. The repeated impact to the nerve in your wrist may cause tingling, pain and weakness in your hand, arm, and shoulder.
Involvement of multiple nerves called polyneuropathy is common. Damage typically begins in the nerves farthest from the central nervous system. Polyneuropathy can be caused by diabetes and other systemic diseases, infections, or exposure to toxic substances.
One or all the three nerve types may be affected. Polyneuropathy can be due to damage to sensory nerves, and can also cause damage to your motor nerves which can result in muscle weakness lack of coordination, twitching and pain.
A common sign of autonomic neuropathy is nerve damage to the internal organs and glands and can include intolerance to heat, loss of bladder control, gastrointestinal disturbances, impairment of breathing and impairment of heart rate.
